ACH money transfers have become a fundamental part of modern financial transactions, offering a secure, cost-effective, and efficient way to move funds electronically. Whether you are an individual receiving your paycheck, a business processing vendor payments, or a government entity distributing benefits, ACH transactions play a critical role in the financial system.
In this guide, we will explore what ACH money transfers are, how they work, and their key differences from other transfer methods like wire and SWIFT payments. We will also discuss their use cases, costs, and how non-U.S. citizens can access the ACH network.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways:
- ACH transfers provide a secure and cost-effective way to send and receive payments electronically in the U.S.
- ACH vs. Other Transfers – ACH is slower but cheaper than wire transfers and primarily used for domestic transactions.
- Use Cases – Commonly used for payroll, recurring bills, B2B payments, and e-commerce.
- Non-U.S. Access – DSGPay offers virtual U.S. accounts, allowing non-U.S. users to receive ACH payments.
- Managing Funds – Users can hold USD, convert to local currencies, and make international payments at lower costs.
What Is ACH?
Automated Clearing House (ACH) is an electronic network that facilitates financial transactions between banks in the United States. It is managed by Nacha (formerly NACHA – The Electronic Payments Association) and is used for direct deposits, bill payments, and other fund transfers.
ACH transactions are processed in batches, making them an efficient and cost-effective method for moving money. The system ensures seamless transactions for individuals, businesses, and government institutions, reducing the reliance on paper-based methods like checks.
How to Send and Receive Payments Using ACH Money Transfers
ACH money transfers provide a reliable and cost-effective method for businesses and individuals to send and receive payments electronically. Whether paying vendors or employees or receiving customer payments, ACH transactions offer a seamless alternative to traditional checks and wire transfers.
Understanding the process of initiating and accepting ACH payments can help streamline financial operations while reducing transaction costs.
Sending ACH Payments
- Gather Recipient Information: Obtain the recipient’s name, bank account number, and routing number.
- Initiate Payment Through Your Bank or Payment Provider: Log in to your online banking or payment provider platform and select ACH transfer.
- Enter Payment Details: Input the amount and recipient details, and specify whether it is a one-time or recurring payment.
- Review and Confirm the Payment: Double-check all details for accuracy before submitting.
- Authorize the Transaction: Confirm and approve the transaction. Processing typically takes 1-3 business days.
- Monitor the Transaction: Track the progress of the payment to ensure it is completed successfully.
- Verify Payment Completion: Ensure the recipient has received the funds as expected.
Receiving ACH Payments
- Provide Your Bank Details: Share your bank account number and routing number with the sender.
- Authorize the Incoming Payment: In some cases, you may need to approve the transaction with your bank.
- Monitor Your Account: ACH payments typically take 1-3 business days to reflect in your account.
- Verify the Funds: Ensure that the received payment is correct and reconcile it with your records.
- Check for Any Holds or Delays: Some banks may place holds on large ACH deposits, so it’s important to confirm when funds will be fully available.
How Do ACH Transfers Work?
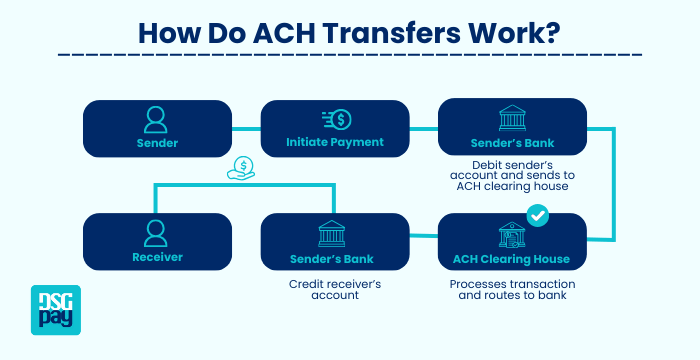
ACH transfers work like a digital check, moving money between banks securely. First, the sender starts the payment through their bank. The sender’s bank takes the money from their account and sends it to the ACH clearing house, which processes the transaction and forwards it to the receiver’s bank. Finally, the receiver’s bank deposits the money into the recipient’s account. This process makes ACH transfers a reliable and cost-effective way to send and receive payments.
What Are ACH Money Transfers?
ACH money transfers are electronic payments processed through the Automated Clearing House network. These transfers are categorized into two types:
- ACH Credit: The sender pushes funds to a recipient, such as direct deposits from employers to employees.
- ACH Debit: The recipient pulls funds from the sender’s account, such as when a utility company collects a bill payment.
ACH money transfers are commonly used for payroll, government benefits, business-to-business payments, and recurring payments like mortgages and subscriptions. They offer a reliable, low-cost alternative to paper checks and credit card transactions, enhancing financial efficiency and security.
What Is the Difference Between ACH and SWIFT Transfer?
ACH and SWIFT transfers serve different purposes and operate in distinct ways:
ACH Transfers
- Used primarily for domestic transactions in the U.S.
- Processed in batches, making them slower (1-3 business days) but cost-effective.
- Best for payroll, bill payments, and recurring transactions.
SWIFT Transfers
- Used for international transactions across different financial institutions worldwide.
- Processed individually, often completed within the same day or up to 5 business days.
- Typically more expensive due to intermediary banks and currency exchange fees.
What Is the Difference Between ACH and Wire Transfer?
ACH and wire transfers both move money between banks, but they differ in cost, speed, and security
ACH Transfers
- Processed in batches and may take 1-3 business days.
- Low or no fees, making them ideal for routine transactions.
- Transactions can be reversed in case of errors.
Wire Transfer
- Processed in real-time, often completed within hours.
- Higher fees (domestic wires cost $15-$30; international wires can exceed $50).
- Irreversible once sent.
What Is the Difference Between EFT and ACH?
Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT) is an umbrella term that encompasses various digital payment methods, including ACH transfers. Other types of EFT include:
- Credit and debit card transactions
- Wire transfers
- Online banking transfers
- Mobile payment apps (Zelle, Venmo, PayPal, etc.)
While all ACH transactions are EFTs, not all EFTs are ACH transactions.

ACH Money Transfers Use Cases
- Payroll Processing: Businesses use ACH to deposit salaries directly into employees’ bank accounts.
- Recurring Bill Payments: Utilities, mortgages, and subscription services use ACH debits for automated collections.
- B2B Transactions: Companies make vendor and supplier payments through ACH transfers.
- Government Payments: Tax refunds, Social Security benefits, and other disbursements are sent via ACH.
- E-commerce Payments: Online businesses use ACH to process bank transfers instead of credit cards.
- Charitable Donations: Nonprofits receive recurring donations through ACH transfers.
- Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Transfers: Apps like Venmo and PayPal use ACH for bank-to-bank transactions.
What Countries Use ACH?
ACH is specific to the U.S., but other countries have similar systems:
- SEPA (Single Euro Payments Area): Europe
- FPS (Faster Payments Service): United Kingdom
- EFT (Electronic Funds Transfer): Canada
- BECS (Bulk Electronic Clearing System): Australia
These systems function similarly to ACH but have different regulatory frameworks and capabilities.
How Much Does International ACH Cost?
International ACH transactions are not standardized, and costs vary based on the service provider and recipient country. Some banks and payment processors charge fees ranging from $5 to $25, while others offer international ACH transfers at no cost if currency conversion is not required. Additionally, exchange rates and intermediary fees may apply.
Can I Use ACH to Send Money Internationally?
ACH is primarily a U.S.-based network and is not designed for international transactions. However, some financial institutions and third-party services offer International ACH Transfers (IAT), which convert ACH payments into international wire transfers. These transactions depend on partnerships with foreign banks and are subject to different fees and regulations. Additionally, cross-border ACH-like networks exist in several countries, offering similar functionality.
How Can Non-U.S. Citizens Use ACH?
Non-U.S. citizens can access ACH transfers by opening a U.S.-based bank account or using financial services that provide virtual U.S. accounts.
DSGPay Virtual Accounts
For individuals and businesses outside the U.S. looking to send and receive ACH payments, DSGPay’s virtual accounts offer a seamless solution. DSGPay provides non-U.S. users with a U.S.-based virtual account, enabling them to:
- Receive ACH payments from U.S. clients and businesses.
- Pay U.S. suppliers and service providers using ACH transfers.
- Reduce transaction costs compared to international wire transfers.
- Enjoy a secure and compliant payment experience.
DSGPay’s virtual account service bridges the gap for global users needing access to the ACH network without requiring a physical presence in the U.S.

How to Set Up a Virtual Account with DSGPay
Setting up a Virtual Account with DSGPay is simple and allows individuals and organizations to receive USD payments without needing a U.S. bank account. Follow these steps to get started:
Opening a DSGPay virtual account allows non-U.S. citizens to access the ACH network seamlessly. Here’s how you can open a DSGPay virtual account to start sending and receiving ACH payments:
- Download the DSGPay App: Go to the Apple App Store or Google Play Store and search for ‘DSGPay’. Download and install the app on your device.
- Sign Up for DSGPay: Create an account on DSGPay’s platform and complete the verification process. This ensures secure and compliant transactions. Provide your personal or business details, including your full name, email address, and country of residence.
- Complete Identity Verification: Submit the required identification documents, such as a passport or business registration, to comply with regulatory requirements.
- Access Your Virtual Account Details: Once approved, log into your DSGPay dashboard to view your Virtual Account information, including Account Holder Name, ACH Routing Number, Wire Routing Number, Account Number, and Bank Name.
- Enter Your Virtual Account Details in Your Platform’s Payment Method:
If you receive payments from platforms like Amazon, go to the payment settings and choose “Direct to U.S. Bank (ACH)” as your withdrawal method. Enter your DSGPay Virtual Account details just as you would with a traditional U.S. bank account. - Receive Your Payments: Once your platform processes the payment, funds will be deposited into your DSGPay account within 2–3 business days. Now, you have the ability to transact efficiently within the U.S. financial system without needing a physical U.S. presence.
- Manage Your Earnings: Once funds are deposited into your DSGPay account, you can optimize your financial transactions in several ways:
- Hold and Withdraw USD: Keep your funds in USD and withdraw when exchange rates are most favourable to maximize your earnings.
- Convert to Local Currency: Easily exchange USD to your local currency, such as PHP, EUR, GBP, etc., and transfer the funds to your bank account with lower fees compared to PayPal or wire transfers.
- Make International Payments: Use DSGPay’s multi-currency options to send money globally, pay suppliers, or manage business expenses efficiently.



