Cross-border payments are transactions where funds move between parties in different countries, typically involving currency exchange. Whether you’re a business paying overseas suppliers or an individual sending money abroad, understanding how these payments work is crucial.
As global trade grows, cross-border payment volumes are rising, reaching over $240 billion in revenue in 2022 and projected to exceed $3 trillion by 2028. With increasing demand for fast, secure, and low-cost international transfers, knowing your options can help you save time and money.
This guide breaks down everything you need to know and how to choose the right solution for your needs.
Table of Contents
What Are Cross-border Payments?
Cross-border payments are international transactions of funds between individuals or businesses located in different countries and using different currencies.
They are commonly used for purposes such as travel expenses, sending money to family and friends abroad, international trade, and investment activities.
So, for instance, if your business has a workforce spread across different countries, cross-border payment solutions could help you pay your employees and manage the payroll securely and efficiently.
Types of Cross-border Payments
Both businesses and individuals can do cross-border transactions that usually involve different currencies. These transactions can broadly be classified as:
Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C) Transactions
These are financial transfers between individuals, typically for personal reasons.
Use Cases
- Sending money to friends or family.
- Gifting money to someone abroad.
Business-to-Business (B2B) Transactions
These are financial transfers between businesses operating in separate countries.
Use Cases
- Importing goods from overseas suppliers.
- Paying for outsourced services
- Making investments in foreign markets.
Consumer-to-Business (C2B) Transactions
Individuals make payments to businesses located in another country.
Use Cases
- Purchasing goods from e-commerce.
- Paying tuition fees for foreign universities.
- Covering healthcare expenses abroad.
Business-to-Consumer (B2C) Transactions
Businesses make payments to individuals across borders.
Use Cases
- Paying salaries to remote employees.
- Issuing refunds to international customers.
- Distributing government benefits to citizens living abroad.
How to Send Cross-border Payments
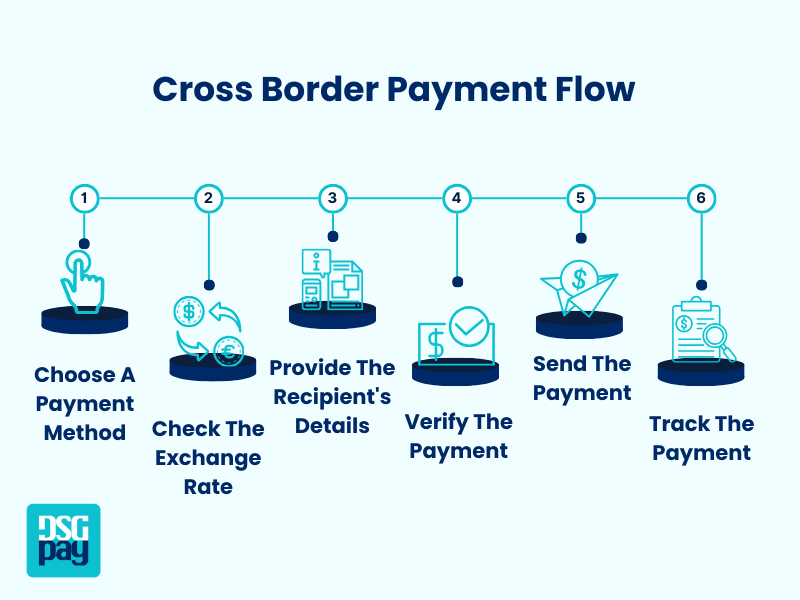
The process of cross-border money transfers will vary depending on your preferred method, but the main steps will generally be as follows:
- Step 1: Choose a Payment Method
- Choose from one of the payment methods mentioned earlier based on your business’s requirements.
- Step 2: Check the Currency Exchange Rate
- Since exchange rates continuously fluctuate, it’s important to know the rate when sending money so that both the sender and recipient understand the amount being transferred.
- Step 3: Fill in the Recipient’s Details
- Provide accurate details, including the recipient’s name, bank account number, address, and other details, to prevent errors.
- Step 4: Verify, Send and Track the Payment
- Review all details of the payment to make sure they’re accurate before confirming the transaction. Depending on the method chosen, the time it takes for the payment to be received will differ. Most payment methods provide tracking tools to monitor transfer status.
Popular Methods for Making Cross-Border Payments
The choice of the cross-border payment method will depend on factors like transaction amount, the currencies, the transaction speed, and the associated fees. It’s best to consider these factors before initiating a cross-border transaction.
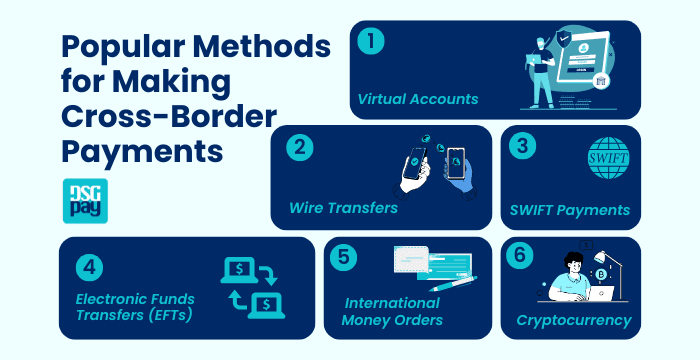
There are several ways to make the payments:
1. Virtual Accounts
Virtual accounts let businesses send, receive, and hold payments in multiple currencies without needing a physical bank account in each country.
They simplify reconciliation, improve cash flow management, and help you collect payments like a local, often with lower fees and faster settlement times compared to traditional banking channels.
2. Wire Transfers
Wire transfers are usually used for large transactions. These are electronic transactions between two financial institutions or banks.
3. SWIFT Payments
The SWIFT network enables secure fund transfers between financial institutions worldwide. Merchants and individuals can receive and send funds via SWIFT.
4. Electronic Funds Transfers (EFTs)
Electronic funds transfers are the electronic transfer of funds between bank accounts without using paper transactions. EFTs can be more convenient than other methods.
5. International Money Orders
International money orders can be purchased at banks. They can be transferred via mail as a paper-based method or electronically through a third-party international payment service.
6. Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency is also a fast and secure option for cross-border transactions, but the volatility of the cryptocurrency market accompanies it.
Key Fees to Consider for Cross-Border Payments
When sending or receiving money internationally, it’s important to understand the full cost of the transaction. Beyond the amount being transferred, several fees can impact the final cost.
Here are the most common charges to watch for:
- Currency Conversion Fees: These fees apply when the sender and receiver use different currencies. These fees vary depending on the currencies involved, the exchange rate markup, and the provider handling the exchange.
- Transaction Processing Fees: Most providers charge a processing fee to cover administrative and risk-related costs. This is typically a percentage of the total transfer amount.
- Foreign Transaction Fees (Card Network Fees): When using credit or debit cards for cross-border payments, card networks often add a foreign transaction fee, usually between 1% and 3% of the payment.
- Intermediary Bank Fees: For SWIFT or wire transfers, one or more correspondent banks may be involved in routing the payment. Each intermediary may deduct a fee from the total amount sent.
- Receiving Bank Fees: Some banks charge the recipient a fee to receive international transfers, especially if the funds are in a foreign currency.
- Fixed Service Charges: Certain platforms apply flat fees per transaction, regardless of the amount sent.
Pros and Cons of Cross-Border Payments
Cross-border payments have become essential for global business and personal transactions. While they offer significant advantages, they also come with a few challenges.
Here’s a quick look at the pros and cons:
Pros
- Increased Revenue: Businesses accepting payments from different countries can expand the reach of their products and services to new international markets. This can increase their revenue and give them a competitive edge.
- Expansion to Global Markets: Cross-border transactions can help businesses engage with new customers, partners, and suppliers in global markets.
- Convenient Customer Experience: Offering the option of cross-border payments can make it easier for customers to pay using their preferred currency and method, be it credit cards or virtual payments. This can allow a business to offer a more personalised experience to customers.
- Portfolio Diversification: Along with the customer base, businesses can diversify and expand their investment portfolio beyond domestic markets with cross-border transactions.
- Cost Saving: By selecting the right payment solutions, you can save money on currency exchange rates, transaction fees, and other fees that come with international trade.
Cons
- Fluctuating Exchange Rates: Changes in the currency exchange rates can affect the final amount the recipient gets, which can be an issue for businesses.
- Fees: As mentioned earlier, international payments usually come with fees. These can make transactions expensive if the most effective cross-border payment company or method aren’t chosen by the business.
- Security Risks: Cross-border payments can be vulnerable to security risks such as cyberattacks, identity theft, payment scams and fraudulent activity. Businesses should protect their transactions by staying updated on data security practices and choosing the right cross-border payment partner that prioritises data security.
- Regulatory Compliance: Cross-border transactions need to navigate regulatory compliance with different countries, such as anti-money laundering (AML), know your customer (KYC), data privacy, consumer protection, and other regulations. This can be complex and time-consuming.
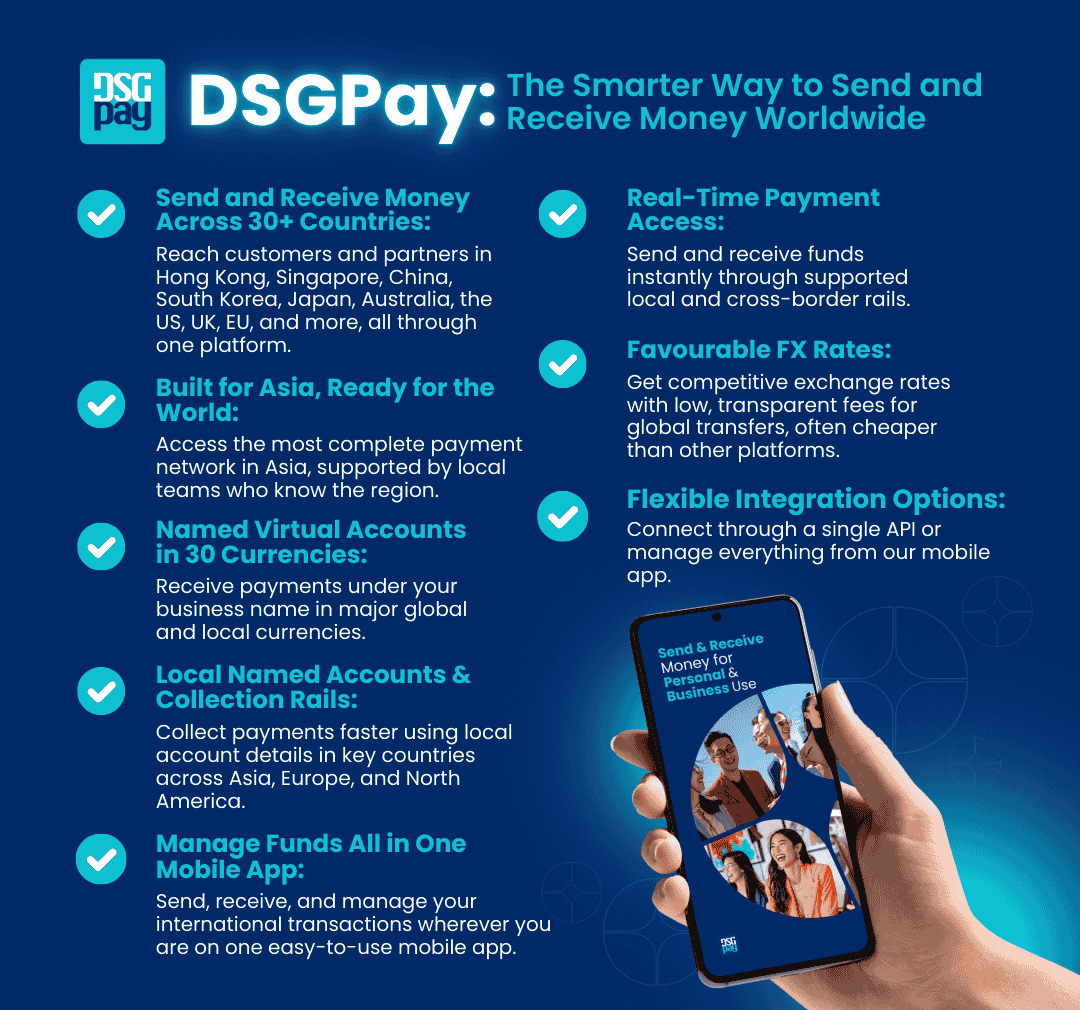
Make Your Cross-Border Payments Easier with DSGPay
Looking for a faster, more affordable way to send and receive money across borders?
DSGPay offers a modern alternative to traditional banking methods, designed for businesses and individuals who need reliable cross-border payment solutions.
Why choose DSGPay for international transactions?
- Global Virtual Account: Open a virtual account that functions like a local account in key markets, making it easy to collect payments from international customers under your business name.
- Support 30+ Currencies: Hold, send, and receive payments in over 30 global currencies without needing multiple local bank accounts.
- Competitive Exchange Rates: Get better value on every transfer with transparent FX pricing and no hidden markups.
- Local & Global Payout Options: Access both local rails (ACH, SEPA, etc.) and global networks (SWIFT) for efficient global disbursements.
- Fast Transaction Processing: Speed up international payments with optimised processing times.
- Compliance & Regulatory Support: Navigate complex global financial regulations with our compliance expertise.
- Real-Time Tracking: Manage, track, and initiate transactions from your mobile device for convenient access anytime, anywhere.
Contact DSGPay today to explore how our cross-border payment services can support your global financial operations.
Concluding Thought on Cross-border Payments
Cross-border payments are no longer just the domain of large corporations. They’re now essential for SMEs, freelancers, global teams, and everyday consumers. As international transactions become faster, more transparent, and more accessible, understanding how they work and how to manage the associated costs is key to staying competitive and financially efficient.
Whether you’re expanding into new markets, paying overseas partners, or receiving funds from abroad, choosing the right cross-border payment solution can make a significant difference in cost, speed, and convenience.
DSGPay offers smarter alternatives to traditional banks. It’s easier than ever to navigate the world of global payments confidently and securely.