Digital financial services in India are at the heart of a significant transformation, reshaping the financial landscape with innovative products and platforms. The significance of this trend is immense and has various implications for the Indian financial sector and the broader economy.
Do you frequently use mobile banking, rely on UPI payments, or explore new fintech platforms? Whether it’s for personal convenience, expanding a business, or accessing credit, digital financial services in India have become an essential part of daily life. These advancements not only simplify financial transactions but also promote economic inclusion and growth.
In this post, we’ll delve into the current landscape, key innovations, and future potential of digital financial services in India, highlighting how they’re shaping the nation’s financial ecosystem and driving economic progress.
Digital Financial Services: The Current Landscape in India
India’s digital financial services sector has undergone remarkable growth, largely driven by technological advancements, increasing smartphone usage, and government-backed initiatives.
For instance, Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana has opened millions of bank accounts, providing access to financial tools for previously underserved populations. Unified Payments Interface (UPI) has emerged as a pivotal platform, handling billions of transactions monthly and making digital payments a norm for individuals and businesses alike. Mobile wallets such as Paytm and PhonePe have further simplified day-to-day financial transactions, enhancing accessibility and convenience.
Moreover, the rural population, which was traditionally excluded from formal banking, is now benefiting from these services. With mobile connectivity expanding, digital financial tools have empowered small merchants, farmers, and self-employed individuals to accept and make payments seamlessly. This shift toward a cashless economy, bolstered by a supportive regulatory framework, has not only driven financial inclusion but also strengthened India’s economic resilience in the digital era.

Types of Digital Financial Services in India
The spread of digital financial services has set the stage for fintech innovation in India. The growth of digital finance has produced a variety of fintech solutions. Here are some examples:
- UPI and QR-Based Payments: The Unified Payments Interface (UPI) revolutionised real-time digital payments in India. Apps like Google Pay and PhonePe leverage UPI, enabling millions to transact instantly. QR code-based payments have made it easy for small vendors and businesses to adopt digital payments without sophisticated infrastructure.
- Credit Access: ZestMoney provides a platform for customers to purchase goods on EMI without a credit card. This innovation has significantly improved financial accessibility for individuals without formal credit histories.
- Digital Lending Platforms: Lendingkart simplifies access to working capital for small and medium enterprises (SMEs). By leveraging data analytics, it evaluates creditworthiness and disburses loans digitally, bypassing traditional hurdles.
- Insurance Marketplace: Policybazaar has streamlined the process of comparing and purchasing insurance policies online, making insurance more accessible and paperless.
- P2P Lending Platforms: Platforms like Faircent connect borrowers and lenders directly, providing individuals and small businesses with quick, low-cost loans while offering investors higher returns.
Digital financial services have been a game-changer in bringing financial services to the unbanked. By offering solutions such as mobile banking and digital wallets, these services empower communities to save, transact, and access credit easily. Initiatives like UPI have simplified payments for small merchants, further driving inclusion.
Contribution to India’s Economic Growth
Digital financial services considerably influence small and medium enterprises, facilitating ease of transactions and access to credit. They also support domestic and international remittances, reducing costs and increasing speed.
The availability and accessibility of digital financial services have a direct and positive impact on the economic growth of a country, as measured by the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and employment rates. Such services provide individuals and businesses with a more efficient, secure, and convenient means of conducting financial transactions, which in turn fosters increased financial inclusion and economic activity.
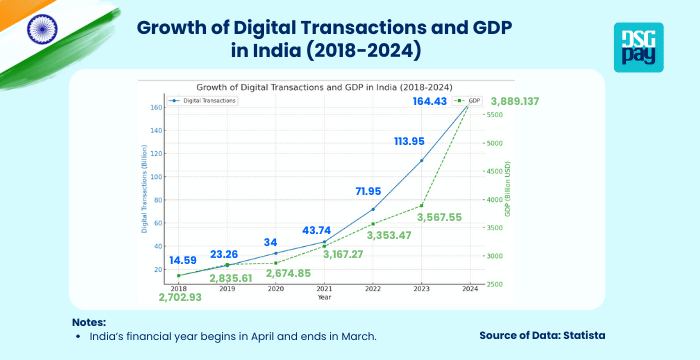
Statista reports that between 2018 and 2024, digital payment transactions in India surged from 14.59 billion to 164.43 billion, showcasing a dramatic shift in the nation’s financial behaviour. During the same period, India’s GDP consistently grew, with current prices projected to increase from approximately $2.70 trillion in 2018 to over $3.88 trillion in 2024.
This correlation highlights how the expansion of digital financial services in India drives economic growth by promoting efficient transactions, financial inclusion, and enhanced productivity across sectors.
Challenges and Risks for Digital Financial Services in India
- Cybersecurity Threats: As more users adopt online platforms, risks such as fraud, phishing attacks, and identity theft have increased, necessitating stronger security measures.
- Data Privacy Concerns: Protecting user data remains a major challenge, especially with the growing volume of sensitive financial information being shared online.
- Regulatory Hurdles: The rapid pace of technological advancements requires regulators to continuously update policies to address emerging risks and ensure compliance.
- Infrastructure Limitations: Rural areas often lack the necessary digital infrastructure, which can hinder the widespread adoption of digital financial services.
- Consumer Awareness and Trust: Building trust and educating users about the safe use of digital platforms is crucial for driving adoption.
The Future of Digital Financial Services in India
India’s financial services sector is experiencing a pivotal shift driven by both domestic advancements and global innovations. Here are five key trends poised to influence India’s economic growth:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning Integration: The integration of AI and machine learning is poised to transform customer service by offering personalized financial guidance, improving fraud detection, and utilizing predictive analytics to support more informed decision-making.
- Blockchain and Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Blockchain technology holds the potential to improve transparency and streamline banking operations, with uses such as secure transactions and smart contracts. Additionally, the growth of DeFi platforms may further broaden access to financial services.
- Embedded Finance: Embedded finance, the incorporation of financial services into non-financial platforms, is set to simplify user experiences by enabling smooth access to services such as payments and lending within routine applications.
- Global Fintech Expansion into India: International fintech companies are preparing to enter the Indian market, bringing with them innovative financial products and services that could increase competition and drive sector growth.
Conclusion
India’s journey in the realm of digital financial services marks a transformative phase in its economic development. With growing adoption and technological advancements, the sector is poised to drive financial inclusion, foster innovation, and boost economic resilience. However, overcoming challenges such as cybersecurity risks, regulatory barriers, and infrastructure gaps will be key to sustaining this growth.
At DSGPay, we specialize in delivering secure and efficient financial solutions tailored to meet the needs of individuals and businesses. We offer multi-currency virtual accounts, enabling access to services in over 30 currencies, including INR, for seamless payments and cross-border transactions. DSGPay is your trusted partner in navigating the evolving digital financial landscape. Reach out to us today to explore how we can empower your financial journey in India.



